download source code here
Create project via Cli
-
Install .net core sdk, .net core runtime at https://www.microsoft.com/net/learn/get-started/windows or https://www.microsoft.com/net/download/windows
in Feb, 2018, .net core sdk is v2.1.4, .net core runtime is v 2.0.5


-
open console,
dotnet new --helpto check templates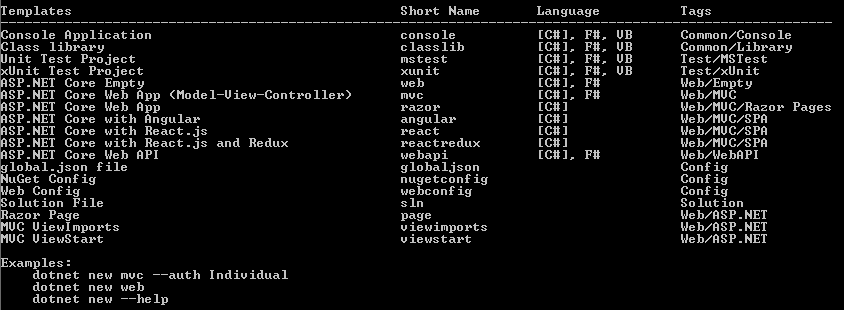
-
create webapi project,
dotnet new webapi -o myApi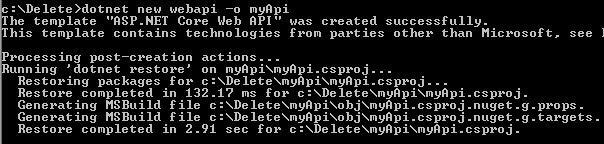
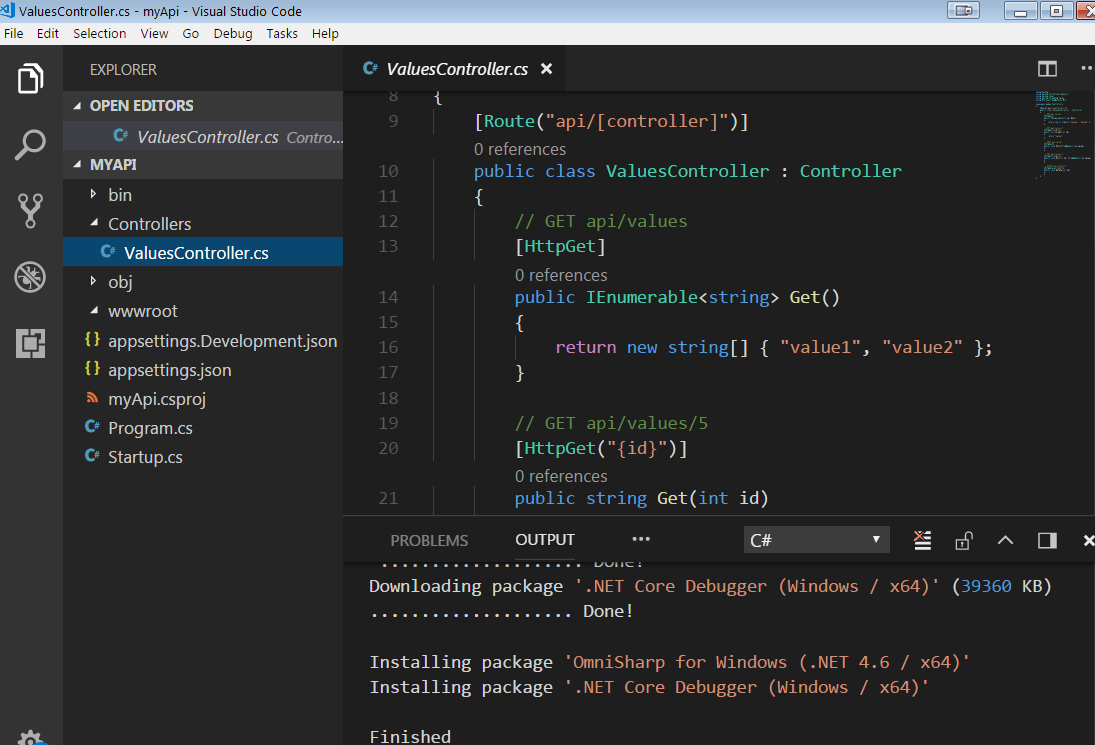
-
run the app,
dotnet run

-
install entity framework core package.
dotnet add Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer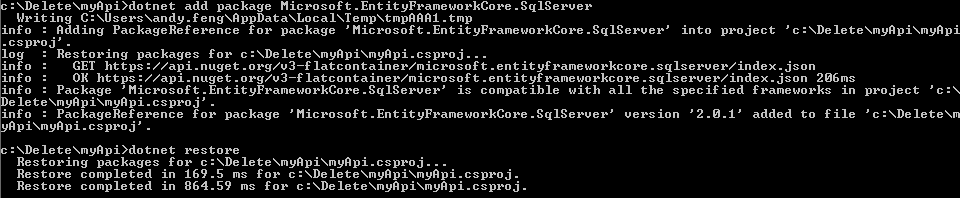
other commands:
dotnet add package: Adds a package reference to the project file, then runsdotnet restoreto install the package.dotnet removepackage: Removes a package reference from the project filedotnet restore: Restores the dependencies and tools of a project.dotnet nuget locals: Clears or lists local NuGet resources such as the http-request cache, the temporary cache, and the machine-wide global packages folder.
Create project via Visual Studio
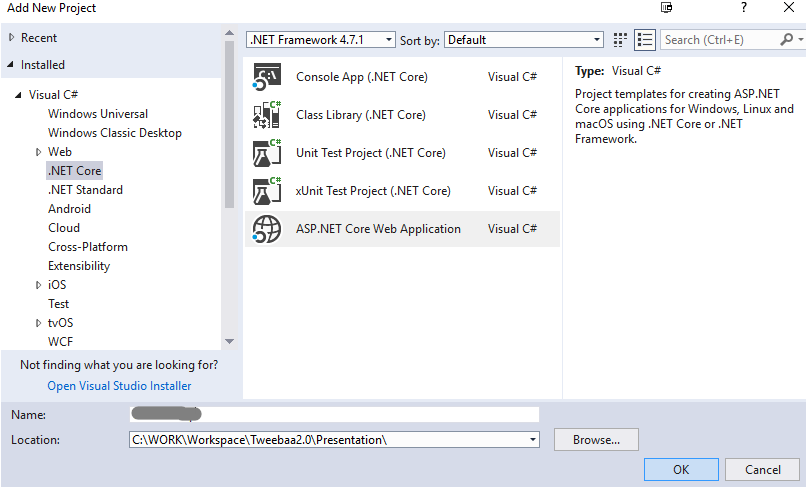
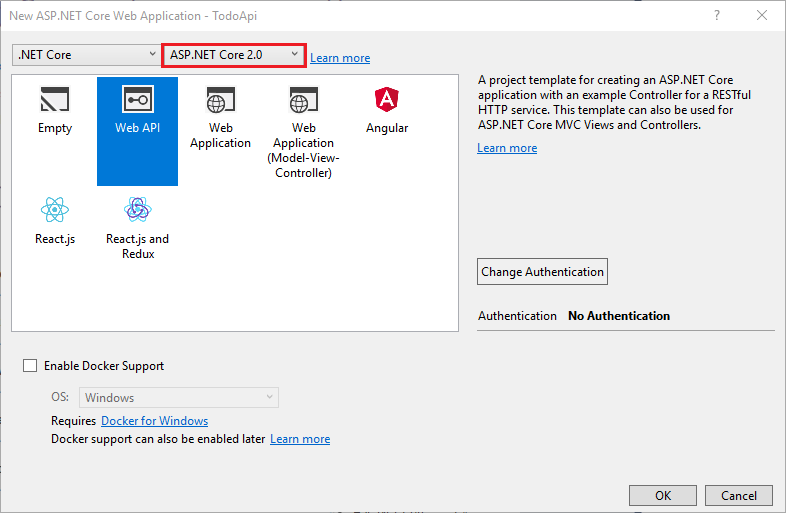
we got

If this webapi project references other libaries, make sure to choose the compatible .net framework version
ctrl + f5 to run,
nuget > install Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer package

Create a simple demo
- add models
Models > TodoItem.cs
namespace Models { public class TodoItem { public long Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public bool IsComplete { get; set; } } } - add data Data > TodoContext.cs: ```csharp using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using Models;
namespace TodoApi.Models
{
public class TodoContext : DbContext
{
public TodoContext(DbContextOptions
public DbSet<TodoItem> TodoItems { get; set; }
} } ```

- register db context in dependency injection container. Here we specify an in-memory database is injected into the service container.
update Startup.cs
public class Startup { public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { services.AddDbContext<TodoContext>(opt => opt.UseInMemoryDatabase("TodoList")); services.AddMvc(); } ... } - Create a controller: TodoController.cs ```csharp using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc; using Models; using Data; using System.Linq;
namespace TodoApi.Controllers { [Route(“api/[controller]”)] public class TodoController : Controller { private readonly TodoContext _context;
public TodoController(TodoContext context)
{
_context = context;
if (_context.TodoItems.Count() == 0)
{
_context.TodoItems.Add(new TodoItem { Name = "Item1" });
_context.SaveChanges();
}
}
} } ```
- Add get endpoints
```csharp
[HttpGet]
public IEnumerable
GetAll() { return _context.TodoItems.ToList(); }
[HttpGet(“{id}”, Name = “GetTodo”)] public IActionResult GetById(long id) { var item = _context.TodoItems.FirstOrDefault(t => t.Id == id); if (item == null) { return NotFound(); } return new ObjectResult(item); }
3. Add create endpoint
```csharp
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult Create([FromBody] TodoItem item)
{
if (item == null)
{
return BadRequest();
}
_context.TodoItems.Add(item);
_context.SaveChanges();
return CreatedAtRoute("GetTodo", new { id = item.Id }, item);
}
- Add update endpoint
[HttpPut("{id}")] public IActionResult Update(long id, [FromBody] TodoItem item) { if (item == null || item.Id != id) { return BadRequest(); } var todo = _context.TodoItems.FirstOrDefault(t => t.Id == id); if (todo == null) { return NotFound(); } todo.IsComplete = item.IsComplete; todo.Name = item.Name; _context.TodoItems.Update(todo); _context.SaveChanges(); return new NoContentResult(); } - add delete endpoint
[HttpDelete("{id}")] public IActionResult Delete(long id) { var todo = _context.TodoItems.FirstOrDefault(t => t.Id == id); if (todo == null) { return NotFound(); } _context.TodoItems.Remove(todo); _context.SaveChanges(); return new NoContentResult(); }
Enable cors
-
Install package
Microsoft.AspNetCore.Corseither via nuget in visual studio or command line
-
Enable cors
-
way1, enable in middleware. modify Startup.cs
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { services.AddCors(); } -
way2, enable in controller
-
Add lazy loading
-
Install package
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Proxies
-
Suppose we have a database
EmployeeManagement, we use database first to generate model classes:Scaffold-DbContext "Server=(local);Database=EmployeeManagement;Integrated Security=True;" Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -OutputDir EntitiesA folder Entities will be created with entities and dbcontext in it
-
Open entity classes, manually set all navigation properties as virtual:

-
Enable lazy loading,
Startup.cs``` ... public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { // add db optoins var connection = @"Server=(local);Database=EmployeeManagement;Integrated Security=true;"; services.AddDbContext<EmployeeManagementContext>(opt => { opt.UseLazyLoadingProxies().UseSqlServer(connection); } ); //services.AddEntityFrameworkProxies(); services.AddMvc().SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_1); } ```
Test
-
run via
dotnet run
-
navigate to
http://localhost:5000/api/todo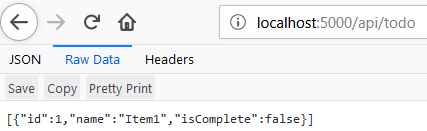
-
post a json data
{ “id”: 2, “name”: “Item2”, “isComplete”: true }
Add database first entities
- Add nuget libraries:
Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer EntityFrameworkCore.Tools EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer.Design -
nuget command console
Scaffold-DbContext "Server=(local)\SQLEXPRESS;Database=EFCoreDBFirstDemo;Integrated Security=True;" Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -OutputDir Entitiesit will create a Entities folder with all models from database inside it.
Enable cors
-
Install
Microsoft.AspNetCore.Corspackage
-
Add the CORS services
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { ... services.AddCors(); } -
Enable cors with middleware. Note that the CORS middleware must precede any defined endpoints in your app that you want to support cross-origin requests (ex. before any call to UseMvc).
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory) { loggerFactory.AddConsole(); if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); } // Shows UseCors with CorsPolicyBuilder. app.UseCors(builder => builder.AllowAnyOrigin().AllowAnyHeader().AllowAnyMethod()); ... }
Model validation
Attribute validation
-
modify properties of model

-
We can define our own validation attribute
public class TorontoPhoneAttribute : System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.ValidationAttribute { protected override ValidationResult IsValid(object value, ValidationContext validationContext) { if(!value.ToString().StartsWith("647")) { return new ValidationResult("this is not 647-xxx-xxxx"); } return null; } } -
In controller, verify
ModelStatus.IsValidand return badrequest accordingly[HttpPost("")] public IActionResult AddCompany([FromBody] TblCompany company) { if (ModelState.IsValid) { this.employeeManagementV2Context.TblCompany.Add(company); this.employeeManagementV2Context.SaveChanges(); return Ok(); } return BadRequest(ModelState); } -
POST a request, we will get errors as below
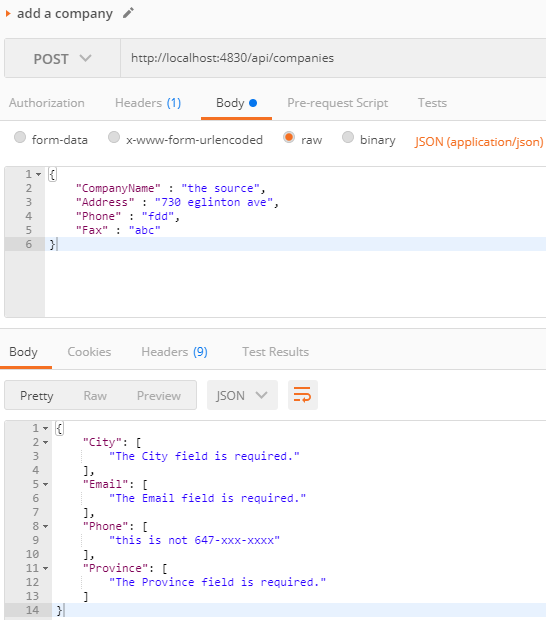
Fluent validation
- Install 3rd package
- asp.net core
FluentValidation.AspNetCore - asp.net mvc
FluentValidation.Mvc5 - asp.net webapi v2
FluentValidation.WebApi
- asp.net core
References
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/tutorials/first-web-api
https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/webdev/2017/04/06/jwt-validation-and-authorization-in-asp-net-core/
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/security/cors
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/mvc/controllers/filters?view=aspnetcore-2.1
https://www.c-sharpcorner.com/article/learn-about-web-api-validation/
https://www.jerriepelser.com/blog/validation-response-aspnet-core-webapi/